Bone edema: what it is, how long it lasts and how it is treated with physiotherapy
or patients with persistent pain after an injury. Although it may sound alarming, it does not always require surgery or prolonged rest, but it does require an appropriate therapeutic approach.
In this article, we explain what bone edema is, why it occurs, how long it can last, and how we treat it through physiotherapy, including techniques such as magnetotherapy.
What is bone edema?
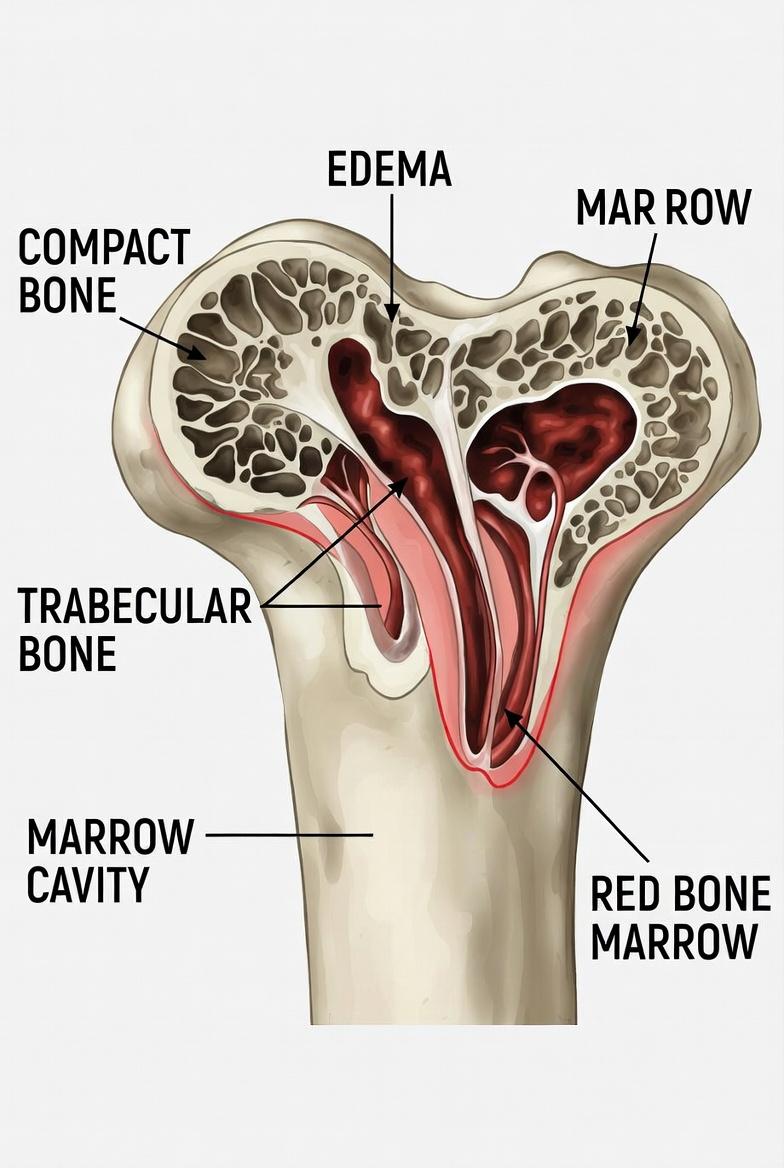
Bone edema is an abnormal accumulation of fluid inside the bone, specifically in the bone marrow. It cannot be seen on standard X-rays and is mainly detected through magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
It is not a lesion in itself, but a sign that the bone is under stress. It may appear in association with trauma, overuse, degenerative processes, or even after surgery.
Most common causes of bone edema
Causes vary depending on the affected area and patient profile, but the most common are:
- Direct trauma (impacts, falls)
- Repetitive overload (running, impact sports)
- Poorly resolved sprains or joint injuries
- Degenerative changes (osteoarthritis)
- Stress fractures
- Post-surgical processes
In many cases, bone edema explains why pain persists even when “everything seems fine” externally.
Common symptoms
The main symptom is usually:
- Deep, localized pain
- Pain that increases with load or impact
- Sensation of stiffness or joint blocking
- Little or no visible swelling (unlike muscle injuries)
It is common for pain not to resolve with short-term rest, which can be frustrating for patients.
How long does bone edema last?
This is one of the most frequently asked questions.
👉 Duration can range from 4 weeks to several months, depending on:
- The cause
- The location
- Load levels
- The treatment applied
Without an appropriate strategy, some bone edemas can become chronic. That’s why early and clinically guided intervention is essential.
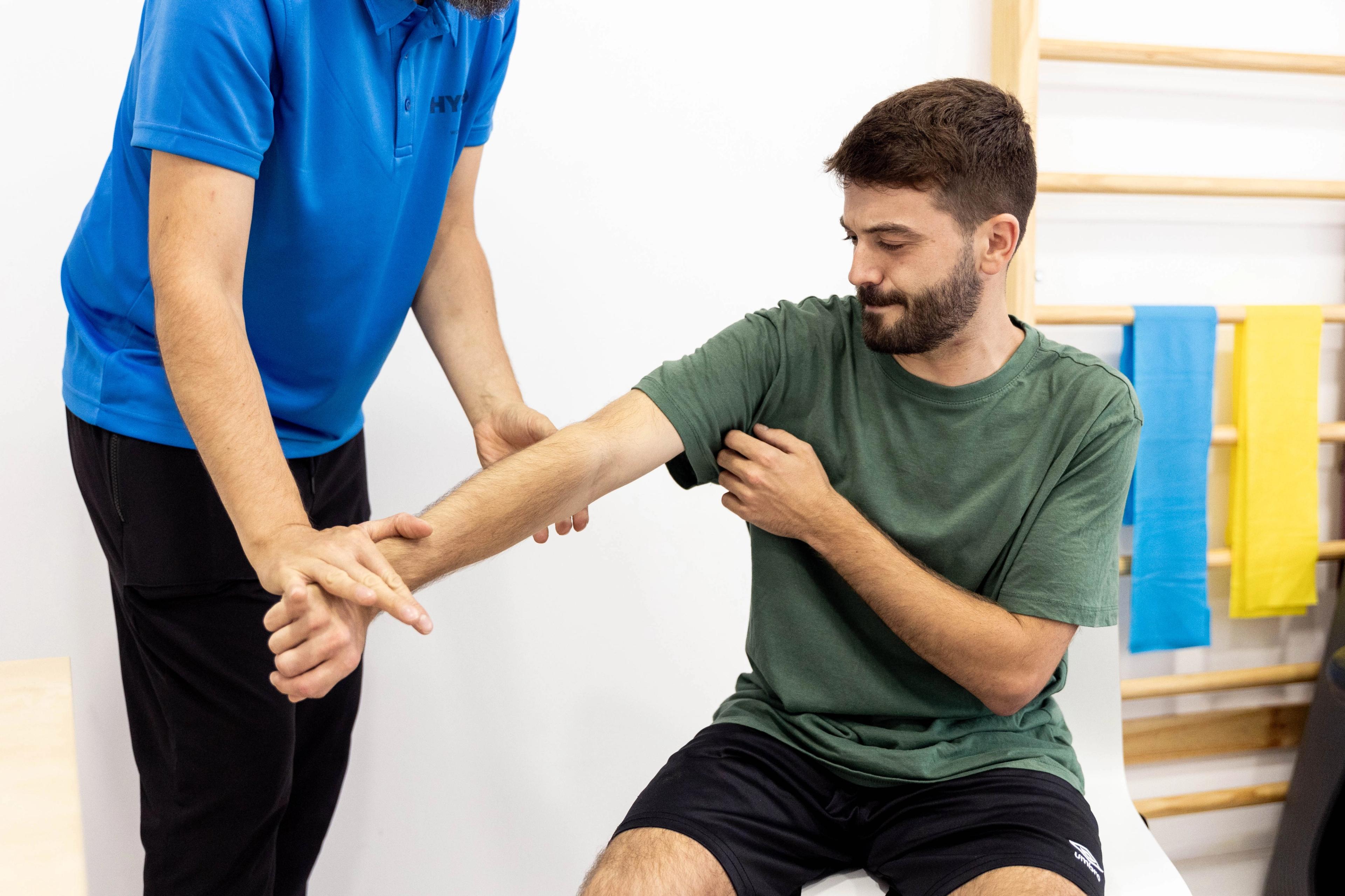
Treating bone edema through physiotherapy
1. Pain and load management
We reduce impact and adjust activity while avoiding unnecessary complete rest.
2. Specific physiotherapy treatment
- Manual therapy
- Progressive therapeutic exercise
- Mobility and joint control work
- Functional reconditioning
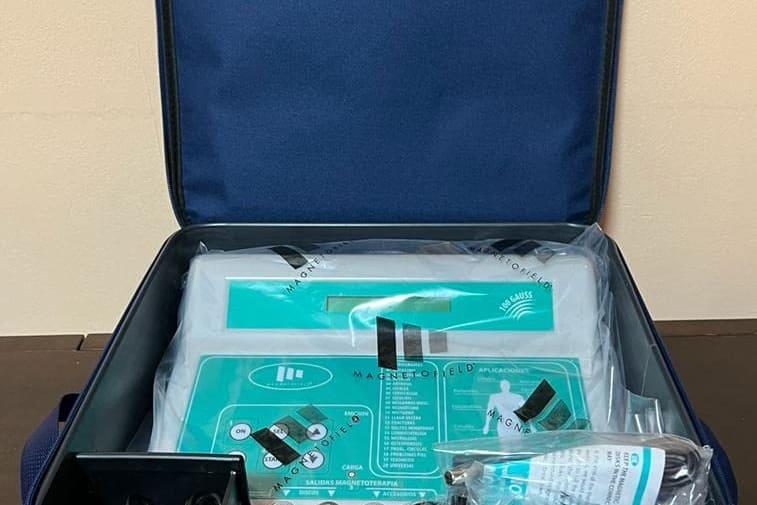
3. Magnetotherapy: a key ally
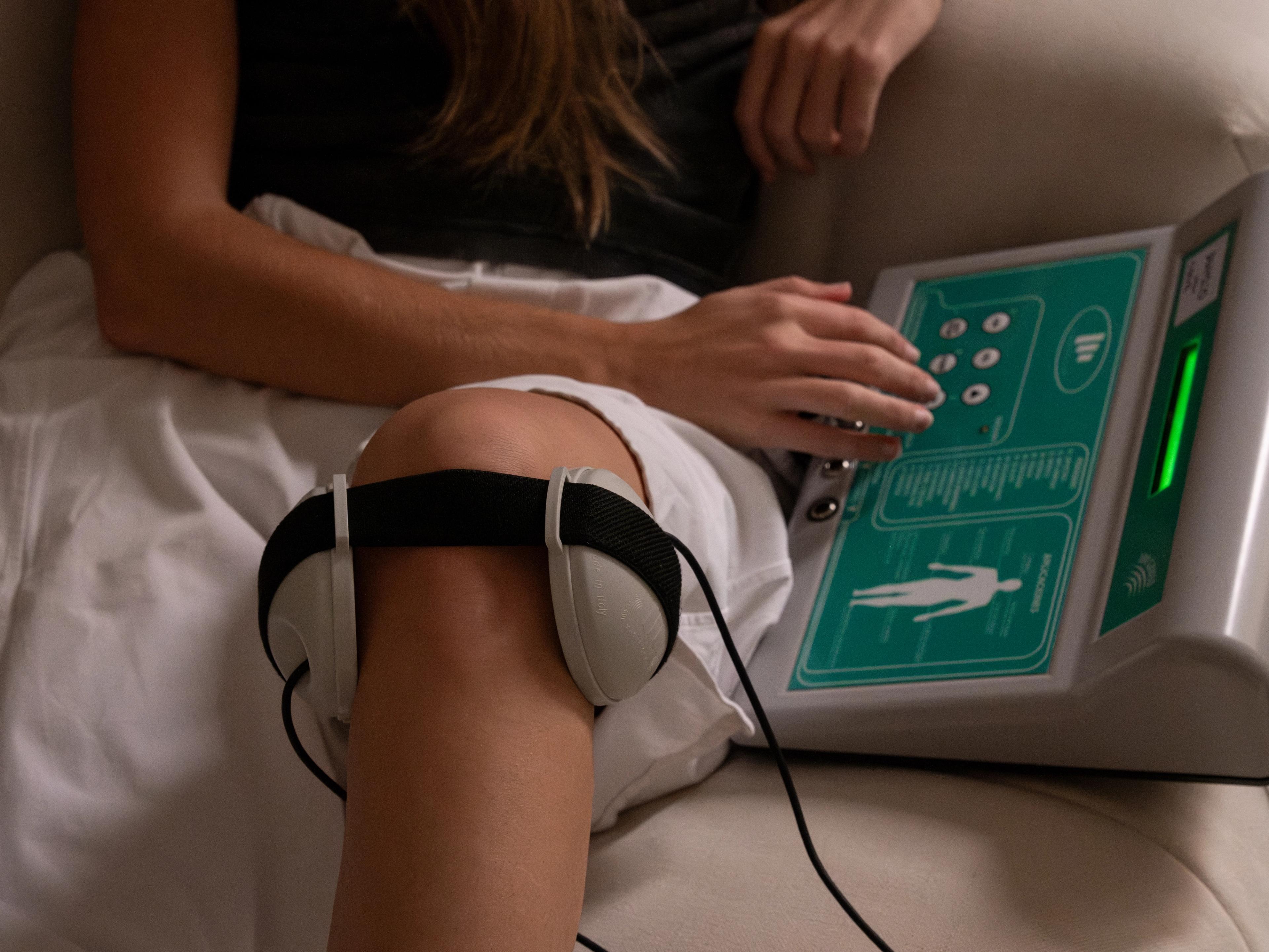

Magnetotherapy uses pulsed electromagnetic fields that promote bone tissue regeneration and help reduce edema and pain.
It is especially effective because:
- It acts directly on bone tissue
- Improves local circulation
- Can be applied daily
- Is painless and safe
In many cases, we combine in-clinic treatment with home magnetotherapy rental, significantly speeding up recovery.
👉 More information here:
Magnetotherapy rental
https://physiowow.com/en/alquiler-magnetoterapia
When should you consult a physiotherapist?
We recommend professional assessment if:
- Pain persists for more than 2–3 weeks
- There is a confirmed MRI diagnosis
- Pain returns when activity is resumed
- You want to prevent the condition from becoming chronic
At our clinics, we work with an individualized approach based on your condition and activity level.
You can visit us at:
- Physiotherapy in Sant Cugat
https://physiowow.com/en/clinicas/sant-cugat - Physiotherapy in Barcelona
https://physiowow.com/en/clinicas/barcelona - Physiotherapy in Sant Joan Despí
https://physiowow.com/en/clinicas/sant-joan-despi

Conclusion
Bone edema should not be ignored or treated with rest alone. With proper diagnosis and a well-planned treatment approach, outcomes are usually positive.
The combination of physiotherapy, load management, and techniques such as magnetotherapy helps reduce recovery time and prevent recurrence, especially in active individuals and athletes.
If you have doubts about your specific case, a professional assessment can make all the difference.

